Repairify’s Guide to ADAS
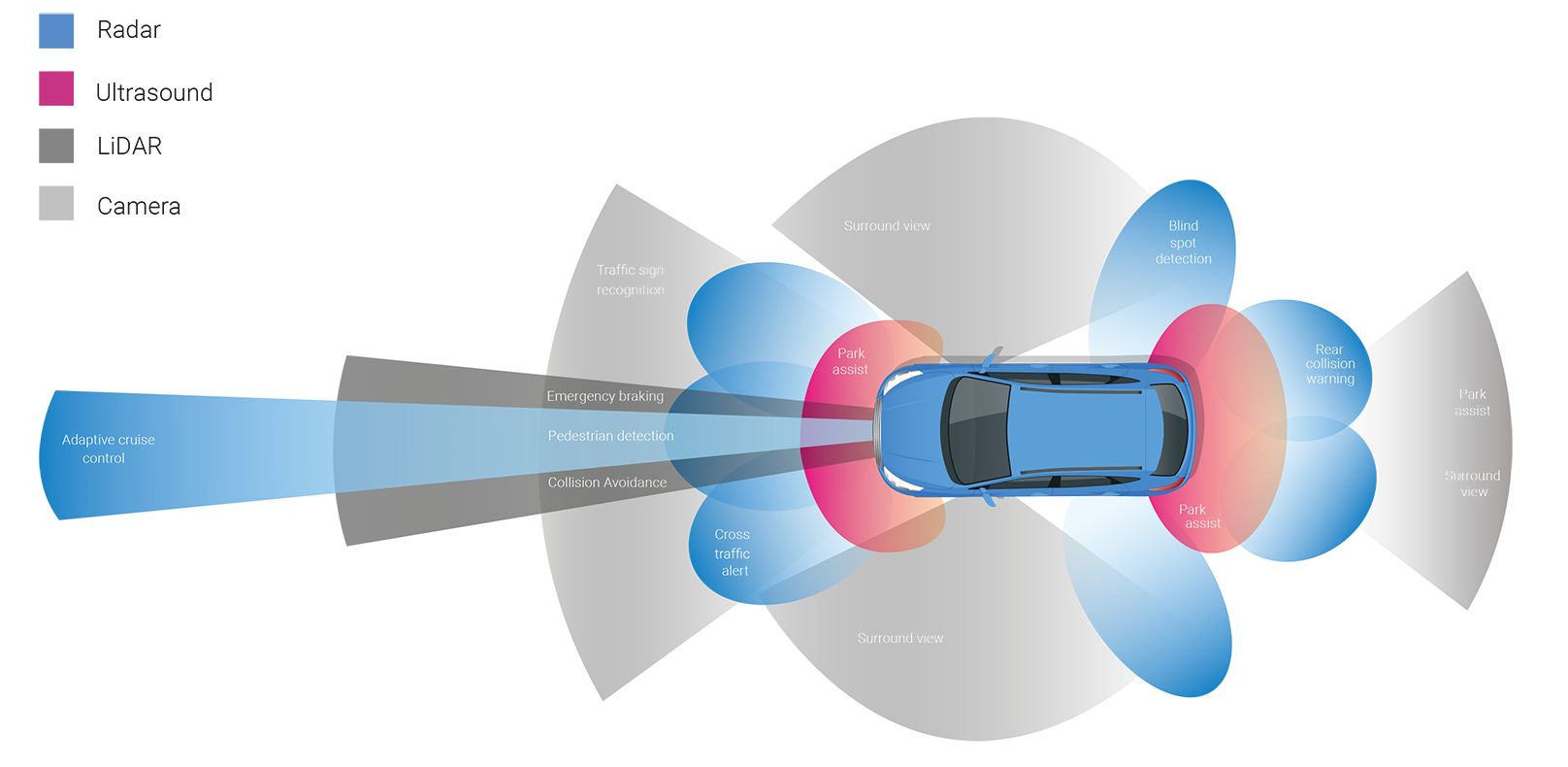
Active Vs Passive ADAS
ADAS systems are either passive or active. Passive ADAS use the sensors to inform the driver of potentially unsafe feedback for the driver to act upon. In an ACTIVE ADAS system, the vehicle takes direct action
The Importance of Calibration
Modern vehicles now feature advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) for improved safety, but this has also increased repair costs due to sophisticated sensors and cameras. Technicians require proper training and tools to recalibrate these components. Vehicles are becoming more like computers, with connected info-tainment systems and over-the-air software updates, raising concerns about cybersecurity and changing risk profiles.
The UK government recently approved its first automated driving system, the Automated Lane Keeping System (ALKS), which can control steering, acceleration, and braking under specific conditions. Under the Automated and Electric Vehicles Act 2018, insurers will be liable for accidents during automated driving mode but can seek compensation from other liable parties.
When is Calibration Required?
ADAS sensor calibration is dictated by OE methodology but is usually required when working in the area of any ADAS related components. Damage to these components can occur in a collision, even a minor bump, or by-product of common service work such as windscreen replacement, suspension repairs or wheel alignment.
The Risks of Not Calibrating
When ADAS systems are incorrectly calibrated, or not calibrated at all, sensors may feedback false information to the ECU which can lead to issues such as not acting or alerting the driver when there is an obstacle. The liability ultimately will fall to the repairer who according to Thatcham’s IIR are responsible for the complete repair of the vehicle. Any collision resulting from incorrectly calibrated ADAS systems can lead to costly legal battles.
We as an industry have to be better at servicing the technology of the future that is assisting us in maintaining safe driving conditions. Every death and serious injury on the road is a preventable tragedy and yet, on average, five people die every day on the road in the UK and 84 are seriously injured.
Thatcham IIR Guidelines
Thatcham Research was established by the motor insurance industry in 1969, with the specific aim of containing or reducing the cost of motor insurance claims while maintaining safety standards.
This insurer funded research centre has involvement and engagement with vehicle manufacturers, regulators, law enforcement organisations, automotive bodies and insurers.
⇒ Identify the presence of ADAS on the vehicle and ensure it is recorded.
⇒ Then, ensure repair procedures clearly identified if inspection, realignment and calibration are required and why.
⇒ Complete all relevant inspection, realignment and calibration activities as retained within the repair procedures.
⇒ Inspection, calibration, realignment and road tests are carried out by a currently competent person.
⇒ Ensure the calibration results confirm that the sensors are functioning within the vehicle manufacturer’s technical specification.
⇒ Produce fully verifiable and auditable records and provide a copy to the asset owner/work provider.
asTech Digital ADAS System
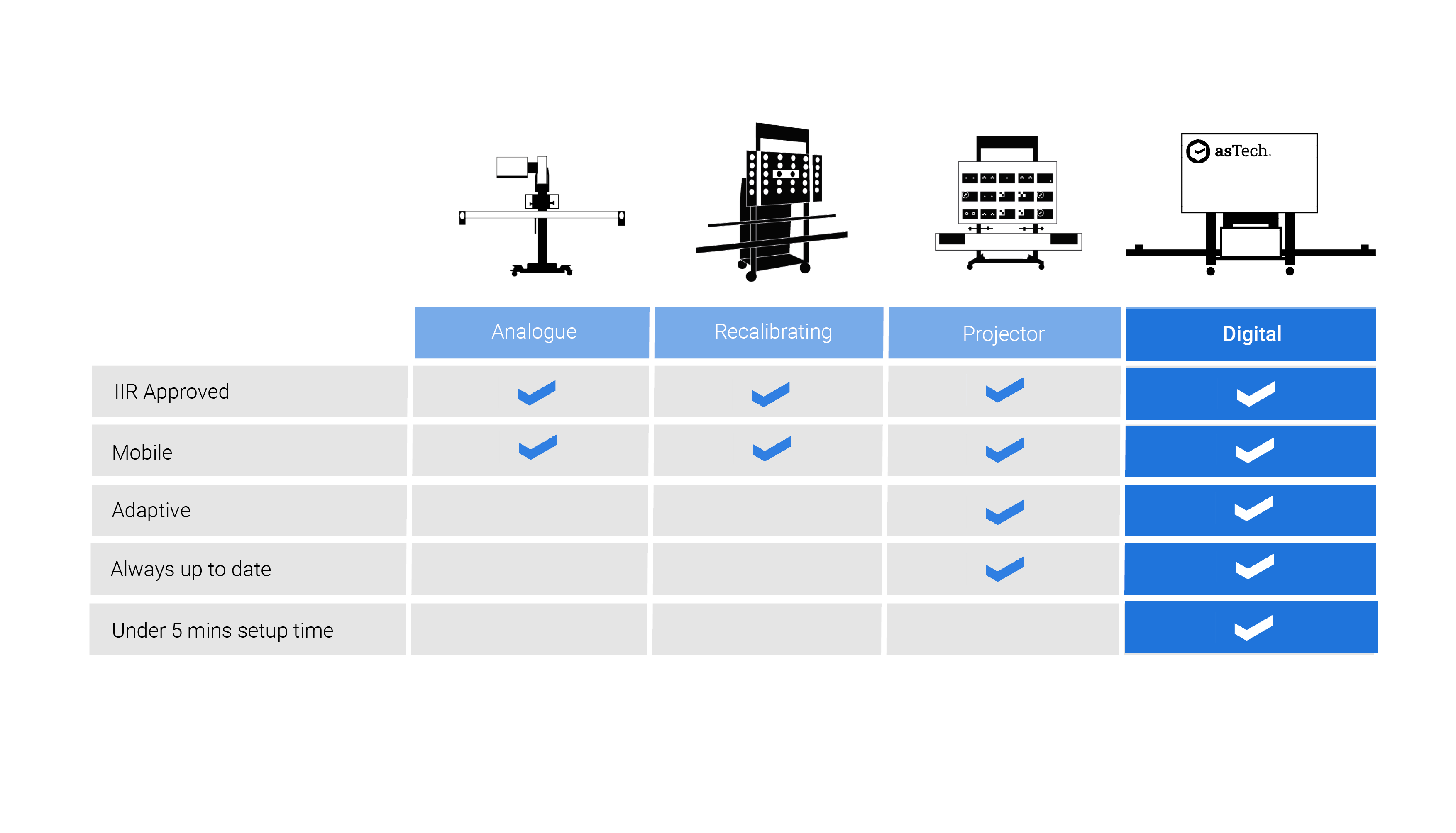
Why go digital?
Boardless System
The digital display allows quick projection of manufacturer targets, reducing set up time and any future targets released are a simple download away – no boards needed.
Easy to Use
Reduced set up time allows calibration in just 6 easy steps.
Keystone Technology
This unique adaptive system adjusts and adapts the target image accordingly to the vehicle. Saving time setting up the calibration equipment and reducing the margin of error.
Universal Coverage
The system covers the most common makes and models and is constantly updated to include the latest vehicles ensuring the largest market coverage meaning no matter what the job is, you can handle it on site.